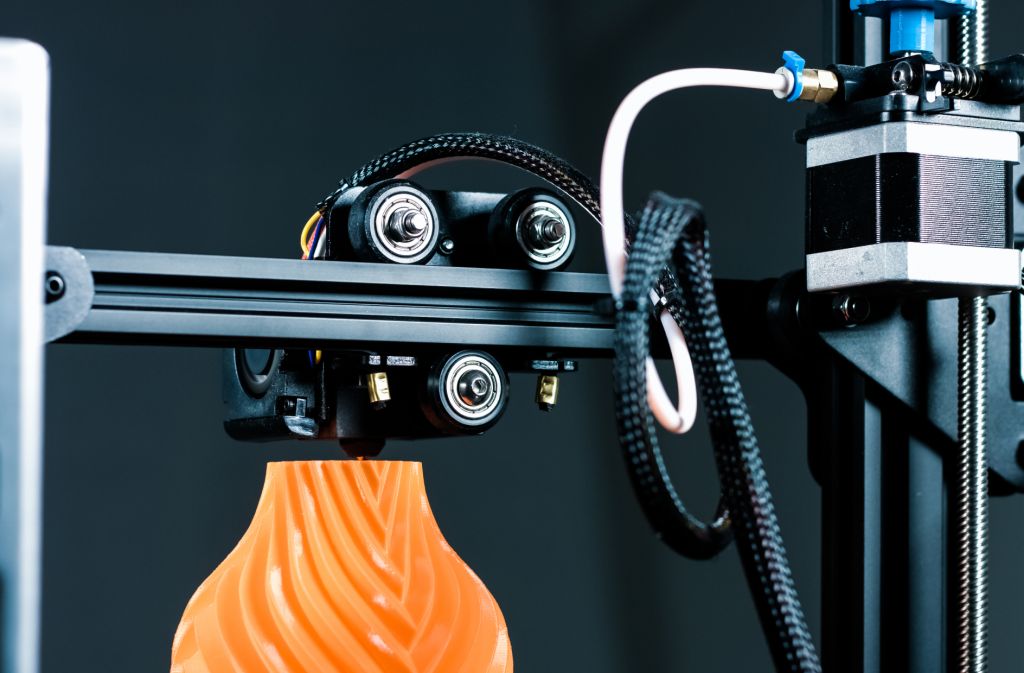
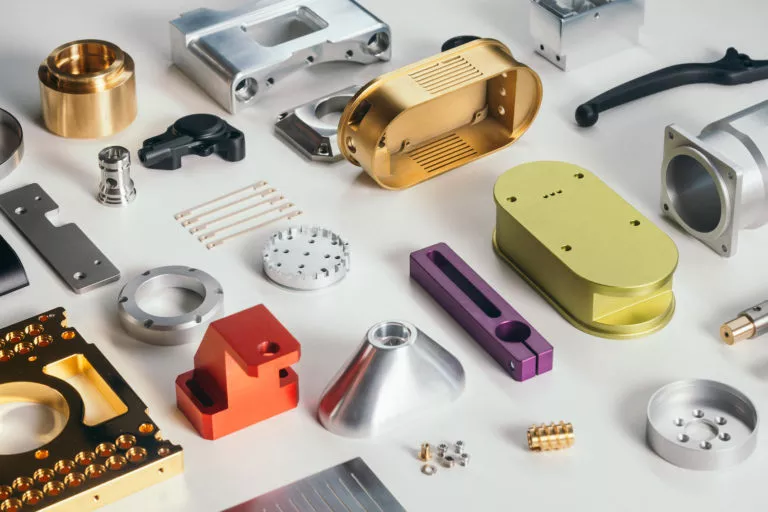
3D printing
Your partner for rapid prototyping and series production in 3D printing. Modern manufacturing in SLS, SLA, FDM and Polyjet process. Attractive prices, wide range of materials and fast delivery. Upload CAD file and receive quote within 48 hours.
1.500+
Satisfied customers
5.500+
Available machines
0,11%
Complaint rate
Audited suppliers
Global network with over 500 audited suppliers
Attractive prices
Highest quality and competitive prices for all manufacturing processes
Fast delivery
With Robtrix you reduce your delivery time by up to 50%
Wide range of materials
All plastics and metals available in over 600 materials
Additive manufacturing in 3D printing
3D printing for rapid prototyping and small batches
Are you looking for a partner for the production of prototypes and small series using the 3D printing process? Our service offers precision and replicability for your desired components. The focus of additive manufacturing at Robtrix is on functional prototypes and small series with fast availability. We support you in rapid prototyping, rapid tooling and in the production of small series.
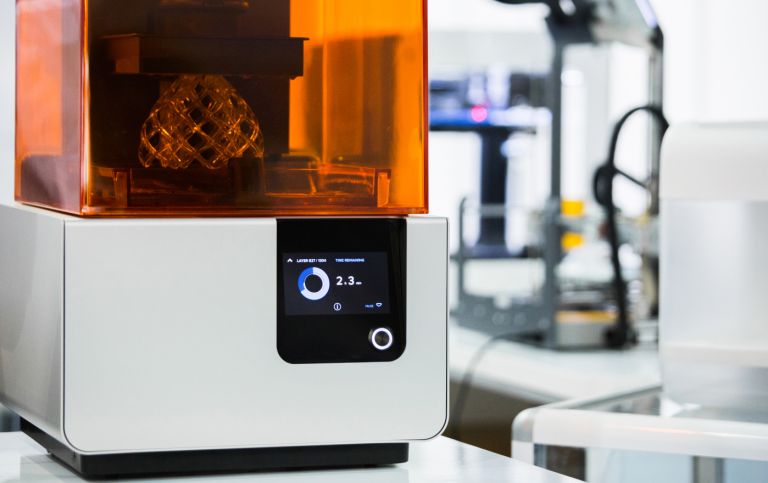

3D Druck
Technical data
| Material thickness: | 0.1 mm – 10 mm |
| Available lengths: | 10 mm – 2.000 mm |
| Tolerances: | +/- 0.1 mm to +/- 0.3 mm |
| Surface finish | 3.2 Ra µm |
| Ideal batch sizes: | 1 – 50.000 pieces |
Our materials
Available materials
| Metals | Plastics |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | PLA |
| Stainless steel | ABS |
| Bronze | Synthetic resins |
| Copper | Nylon |
| Inconel | PETG |
| Titanium | TPU, TPU Ultrasint |
| PA11, PA12, PA12 GF/GB |
For functional prototypes and tools
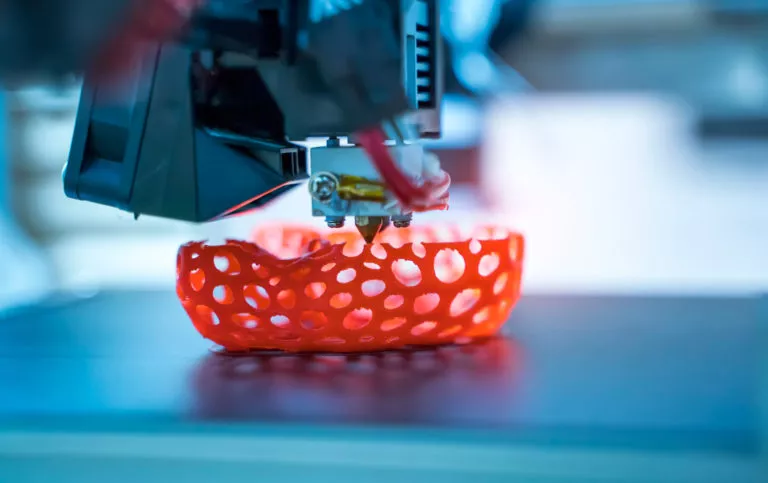
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
In this 3D printing process, a plastic wire, also known as filament, is melted in the hot end of the FDM printer and applied to the print bed in layers. Only materials that can be liquefied or deformed under heat can be used. The soft printing materials are applied layer by layer and harden again after cooling. Suitable materials for this purpose include thermoplastics such as ABS, PLA, PVA, HIPS, PET, nylon and numerous other filaments based on metals, stone and more.
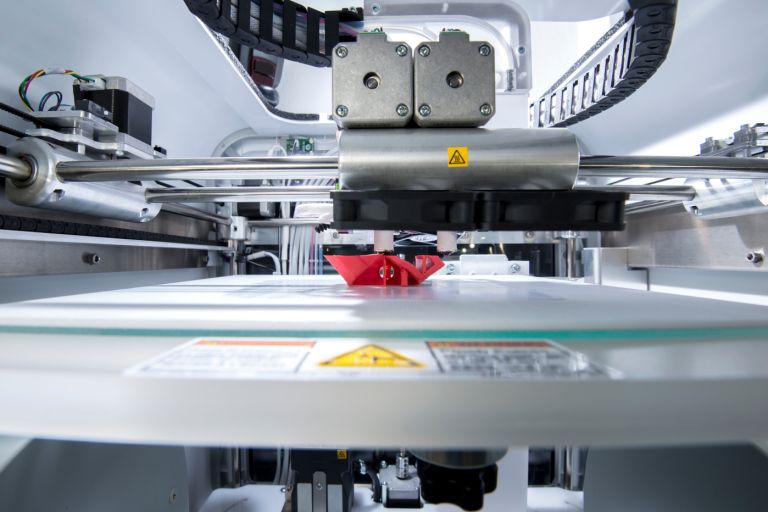

Briefly explained
How 3D Printing Works
The term 3D printing is a comprehensive term for additive manufacturing techniques in which material is applied layer by layer to create a three-dimensional workpiece.
3D printing is used especially for rapid prototyping, rapid tooling and for the production of smaller series. The most important manufacturing methods in 3D printing at a glance.
Combination of materials and colors
Polyjet process (Multijet Modeling MJM)
In the Polyjet process, a print head applies very fine droplets of a photopolymer to a platform, where they are immediately cured using UV light.
Ultra-thin layers (up to 14 μm) can be processed using Polyjet. A very high level of detail with surfaces that are very close to injection molding are possible. During production, different materials can be used in the printing process and also mixed, which enables completely new material properties.
Polyjet printing is therefore a very versatile process that offers a wide range of applications in prototyping.

Why Robtrix
Your advantages
- Flexible and free capacities at any time
- Attractive prices for all components
- Quality control according to ISO 9001:2015
- One contract and contact person for all manufacturing processes
- Digital processes with personal contact person
- Global Supply Chain with German Quality Standards 🇩🇪
You have the choice
Our delivery times
- Offer within 48 hours
- Standard production in 15-20 working days
- Express service in 6-12 working days
For components with complex geometries
Stereolithography (SLA)
A basin filled with liquid photopolymer resin (also called resin), serves as the basis of the SLA process. The photosensitive material is cured at the predefined locations using a UV laser. The platform is lowered as soon as a shift is finished and the process starts again.
Since the workpiece is in a bath of liquid during manufacturing, support structures become necessary. The supports enable the precise production of components with highly complex geometries. SLA printers are therefore even suitable for use in medical technology.
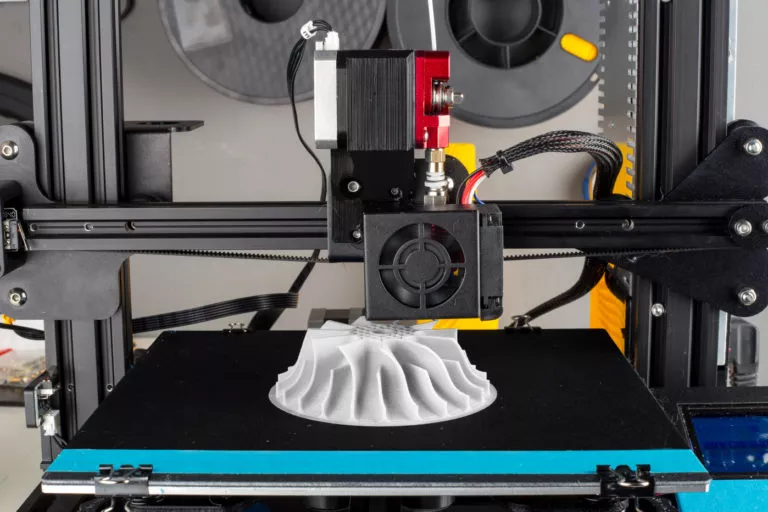
Powder based 3D printing
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
As a powder bed-based 3D printing process, selective laser sintering (SLS) is used in particular for the production of prototypes and finished components made of plastic and metal.
SLS 3D printers work similarly to SLA machines by creating parts with lasers. Instead of resin, however, the component layers in SLS printing are created by sintering powder layers that are applied layer by layer.
A wide range of materials can be processed in the SLS 3D printer with high accuracy, making them ideal for industries such as aerospace and automotive.
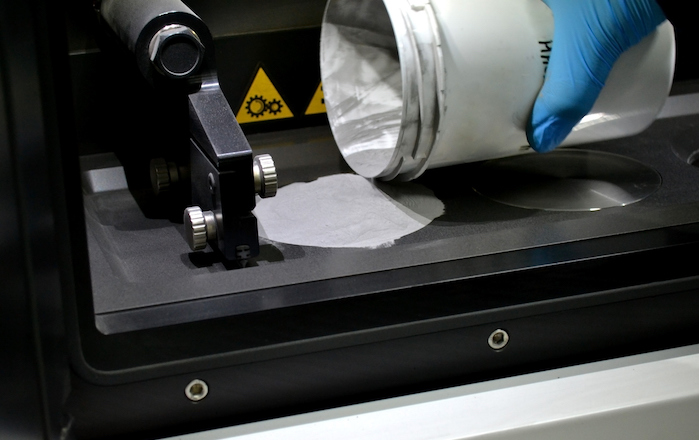
Surface treatment
We get the best out of your components
Refinement, appearance, protection against wear and corrosion prophylaxis of the turned components are as much part of our core business as the production of components.
- ✔ Sandblasting
- ✔ Paint
- ✔ Anodizing
- ✔ Powder coating
- ✔ Electroless nickel
- ✔ Galvanizing
- ✔ Passivate
- ✔ Chromate

